8 Photogrammetry Software Considerations All Drone Operators Should Know
When evaluating any type of software, there are several factors to consider. Technical specifications are obviously important because you need the software to deliver specific outcomes. However, other factors are also important. How easy is it to learn the software? Does how you use it impact the pricing? Should you buy an on-premise solution or rely on cloud-based software? This is especially true for photogrammetry software.
8 Considerations for Photogrammetry Software
In addition to referencing review platforms, such as the G2 Grid for Photogrammetry, for objective feedback, let’s explore some of the factors you should consider when selecting photogrammetry software.
1. Map Outputs
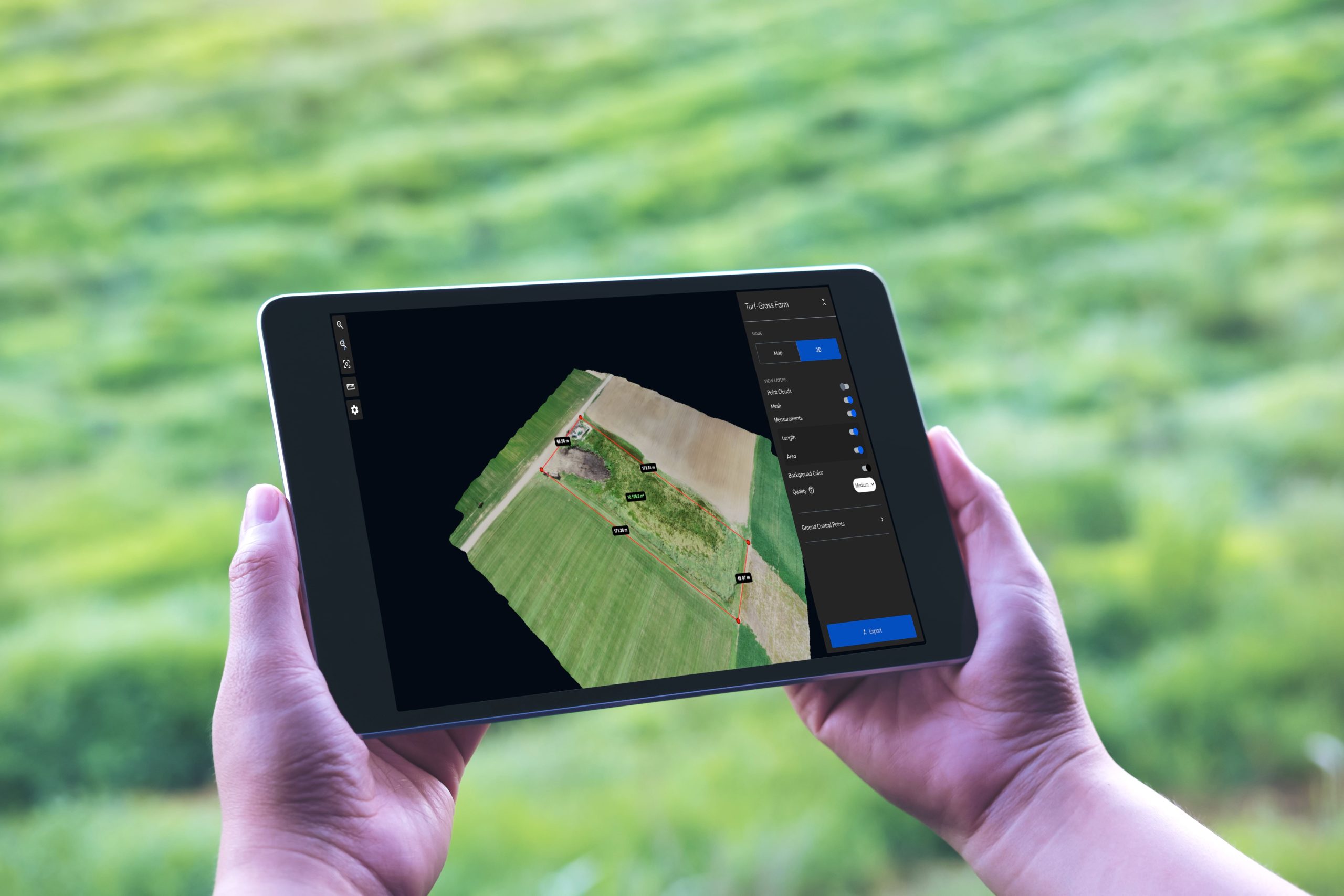
Make sure the software you choose will meet your mapping needs. Look for the ability to create 3D models, digital elevation models, and orthomosaics. You might also need export formats such as:
- Dense point cloud (.las)
- Digital elevation model (.tiff)
- Orthomosaic (.tiff)
- Mesh and texture (.obj)
If you need to use measurement tools, look for high levels of accuracy with ground control points, scale constraints, GPS corrections, and the ability to set the number of objects to detect and match vector preferences.
2. User Interface
The faster you can learn photogrammetry software, the faster you can get your drone—and your project—off the ground. The user interface for your photogrammetry software should be easy to use, allowing you to focus on operating the drone, not on navigating unwieldy software. Make sure you can also easily manage users and access so your teams can work together from any location.
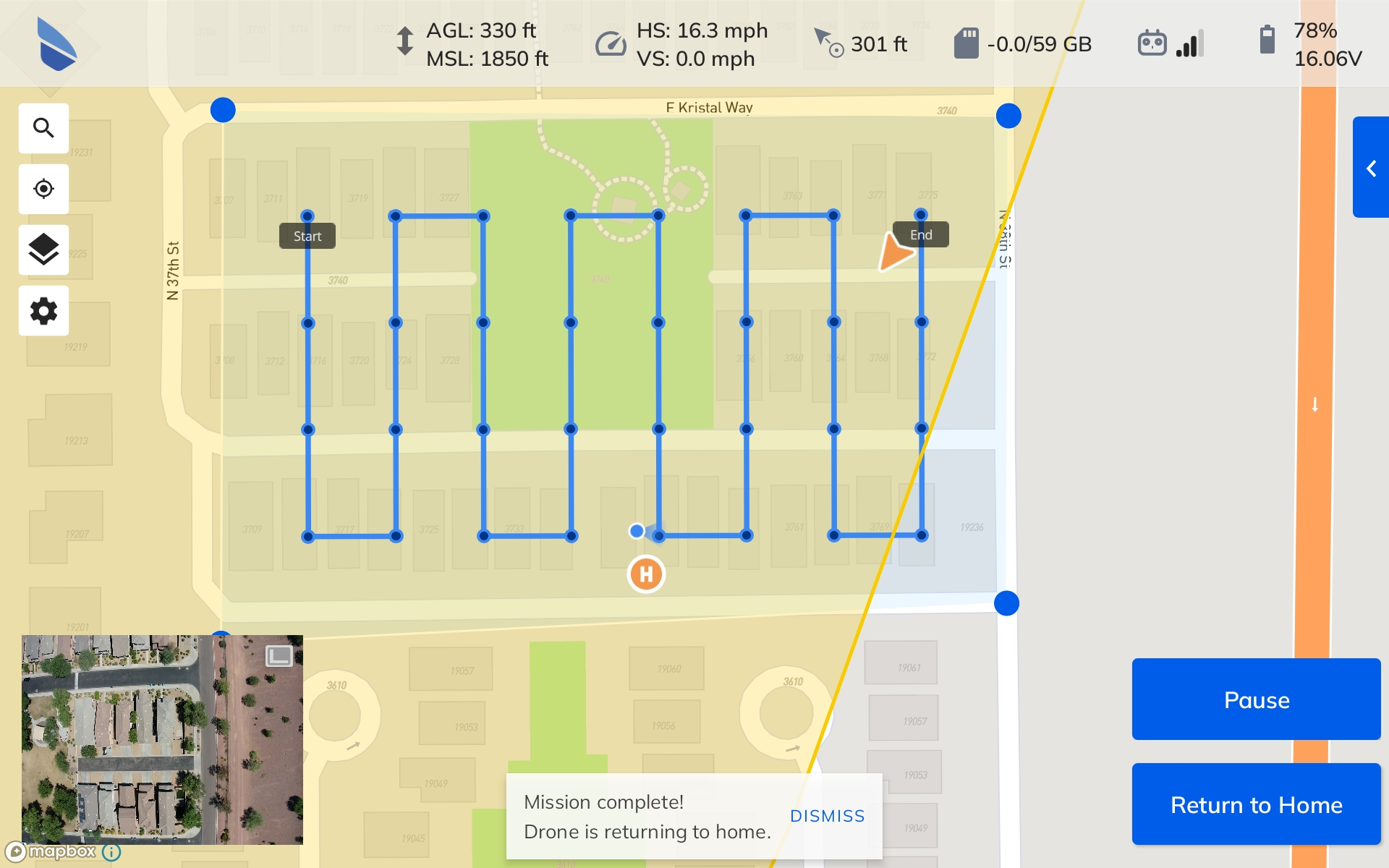
3. Cloud-Based or On-Premise
Consider your existing resources when evaluating photogrammetry software. On-premise software may come with hardware requirements you can’t meet without upgrading, which adds to the cost.
Cloud-based software can be used on phones, tablets, or desktop computers, and you can access it anytime from any machine that can connect to the internet. This gives you ultimate flexibility, doesn’t burden your machine when creating models, and allows you to process more data faster and with fewer crashes. Cloud-based solutions also allow you to avoid a large up-front investment in purchasing on-premise software, servers, and hardware upgrades.
4. Software Integrations
With the right integrations, maps created using photogrammetry software can be used with other software to help you make informed decisions. Export the file type that makes the most sense for your application and import it into the software you already use. For example, engineers overlay buildings designed using computer-aided design on accurate images of the site to see 3D models of the designs in the real world.
5. Storage
Compare storage limits when choosing photogrammetry software because it can impact the overall price, especially if it’s a hidden cost you didn’t anticipate. It’s also important to know how long your data will be stored, so find out if the company you’re considering puts a time limit on it. Understand the costs of storing your data and how you will be billed for it so you can incorporate it into your budget.
Cloud storage allows you to access your data from anywhere so you can always deliver in today’s flexible work environment. Depending on the nature of your project, you may also need a solution that offers secure storage. Look for real-time network monitoring, unified threat monitoring, and dynamic packet filtering to protect your data.
6. Support Resources
Look for a platform that offers free resources that allow you to learn as much as you can on your own. For example, a knowledge base enables you to get fast answers to the most common questions without having to reach out to customer support. You might also want the flexibility of custom configuration services that make your workflow easier and adapt to the way your team already works.
7. Pricing Plans
Flexible pricing plans allow you to choose what makes the most sense for the way you’ll be using the software. If you will be an infrequent user, you might want to start with a plan designed for a single user. If you plan to use the software on a regular basis or need to share information among teams, look for a platform that offers unlimited use with a monthly subscription.
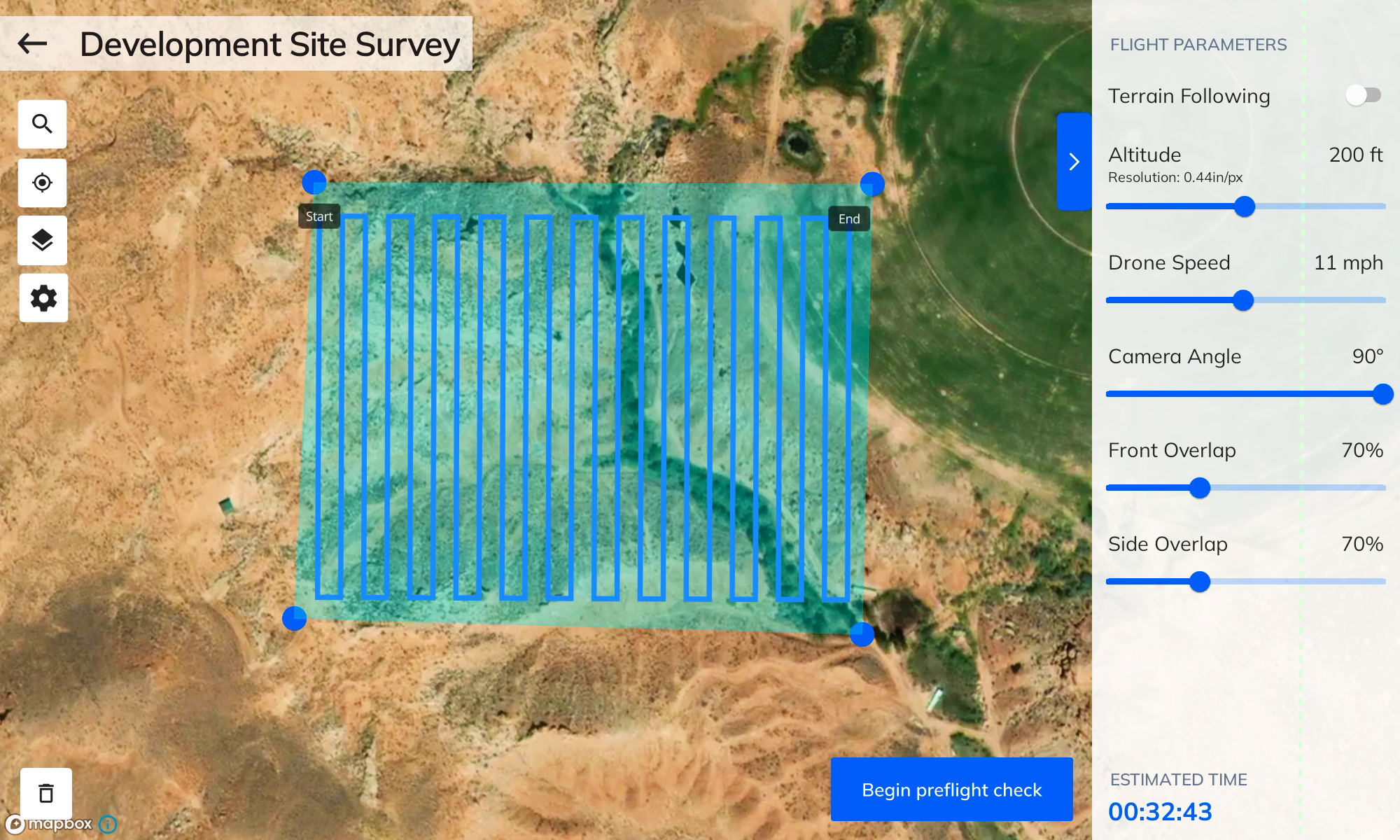
8. Flight Planning and Capture Tools
When evaluating photogrammetry tools, consider whether they come with complementary software that allows you to plan flights or sync captured images with your software. Apps that are integrated with your photogrammetry software can help reduce mistakes, saving you time and money.
As you explore your options, sign up for free trials so you can try before you buy and make sure it’s the right fit for your needs.
Mapware Photogrammetry Software
If you are evaluating various platforms, take a deeper dive into what Mapware has to offer. As a leader on the G2 Grid, Mapware is a proven photogrammetry solution. Hosted on a stable cloud-based platform with GPU-accelerated processing, Mapware is fast, secure, and accessible from anywhere. The intuitive user interface and configurable enterprise tools allow your team to hit the ground running. Flexible pricing plans with no data limits allow you to plan around your budget with no nasty surprises.
Ready to put Mapware to work for you? Start a free trial today!